Huawei Mobile Services
Integrate Huawei Mobile Services in your app to support Engagement push notifications on Huawei devices
Newer phones manufactured by Huawei come with Huawei Mobile Services (HMS) - a service that delivers push notifications instead of Google's Firebase Cloud Messaging (FCM).
To be able to send push notifications from the Engagement platform and receive them in your app on Huawei devices, you must set up Huawei Mobile Services (HMS), implement HMS in your app, and configure the Huawei Push Service integration in the Engagement web app.
The SDK provides a push setup self-check feature to help developers successfully set up push notifications. The self-check will try to track the push token, request the Engagement backend to send a silent push to the device, and check if the app is ready to open push notifications.
To enable the setup check, set
Exponea.checkPushSetup = truebefore initializing the SDK.We suggest you turn the self-check feature on while implementing the push notifications for the first time or if you need to do some troubleshooting.
Set up Huawei Mobile Services
First, you must set up Huawei Mobile Services:
- Register and set up a Huawei Developer account.
- Create a Project and App in AppGallery Connect.
- Generate and configure a Signing Certificate.
- Enable Push Kit in AppGallery Connect APIs.
- Update Gradle scripts and add generated
agconnect-services.jsonto your app. - Configure the Signing Information in your app.
For detailed instructions, please refer to Preparations for Integrating HUAWEI HMS Core in the official HMS documentation.
Implement HMS Message Service in your app
Next, you must create and register a service that extends HmsMessageService. The SDK's automatic tracking relies on your app providing this implementation.
This implementation is not included in the SDK in order to keep it as small as possible and avoid including the libraries that are not essential for its functionality. You can copy the example code below and use it in your app.
-
Create the service:
import android.app.NotificationManager import android.content.Context import com.exponea.sdk.Exponea import com.huawei.hms.push.HmsMessageService import com.huawei.hms.push.RemoteMessage class MyHmsMessagingService: HmsMessageService() { private val notificationManager by lazy { getSystemService(Context.NOTIFICATION_SERVICE) as NotificationManager } override fun onMessageReceived(message: RemoteMessage) { super.onMessageReceived(message) if (!Exponea.handleRemoteMessage(applicationContext, message.dataOfMap, notificationManager)) { // push notification is from another push provider } } override fun onNewToken(token: String) { super.onNewToken(token) Exponea.handleNewHmsToken(applicationContext, token) } } -
Register the service in
AndroidManifest.xml:<service android:name="MyHmsMessagingService" android:exported="false"> <intent-filter> <action android:name="com.huawei.push.action.MESSAGING_EVENT"/> </intent-filter> </service> <meta-data android:name="push_kit_auto_init_enabled" android:value="true"/>
The SDK will only handle push notification messages sent from the Engagement platform. A helper method Exponea.isExponeaPushNotification() is also provided.
After running your application, the SDK tracks the push token to the Engagement platform. If you enabled the self-check feature, it will confirm successful tracking.
You can also verify token tracking manually by locating the customer in the Bloomreach Engagement web application:
- SDK versions below 4.6.0: Check the customer property
huawei_push_notification_id - SDK versions 4.6.0 and higher: Check the
notification_stateevent with propertypush_notification_token
❗️Important
SDK versions 4.6.0 and higher use event-based token tracking to support multiple mobile applications per project. Learn more about Token tracking via notification_state event.
A push token is typically generated at the first application start, but it has its own lifecycle. Your HmsMessageService implementation is triggered only if a token is created or its value has changed. Please validate your expectations against the defined token update triggers
As of Android 13 (API level 33), a runtime notification permission must be registered in your
AndroidManifest.xmland must also be granted by the user for your application to be able to show push notifications. The SDK takes care of registering the permission. However, your app must ask for notification permission from the user by invokingExponea.requestPushAuthorization(context). Refer to Request notification permission for details.If your marketing flow strictly requires normal push notifications usage, configure the SDK to track only authorized push tokens by setting Configuration for Android SDK requirePushAuthorization to
true. Refer to Require notification permission for details.
If you are integrating the SDK into an existing project, you may face an issue that your
HmsMessageServiceis not called automatically.To retrieve a fresh push token, consider requesting a token manually as soon as possible after after application start:
Refer to Obtaining and Deleting a Push Token in the HMS documentation for instructions on how to retrieve the current push token.
The methods
Exponea.handleNewTokenandExponea.handleRemoteMessagecan be used before SDK initialization if a previous initialization was done. In such a case, each method will track events with the configuration of the last initialization. Consider initializing the SDK inApplication::onCreateto make sure a fresh configuration is applied in case of an application update.
Configure the Huawei Push Service integration in Engagement
-
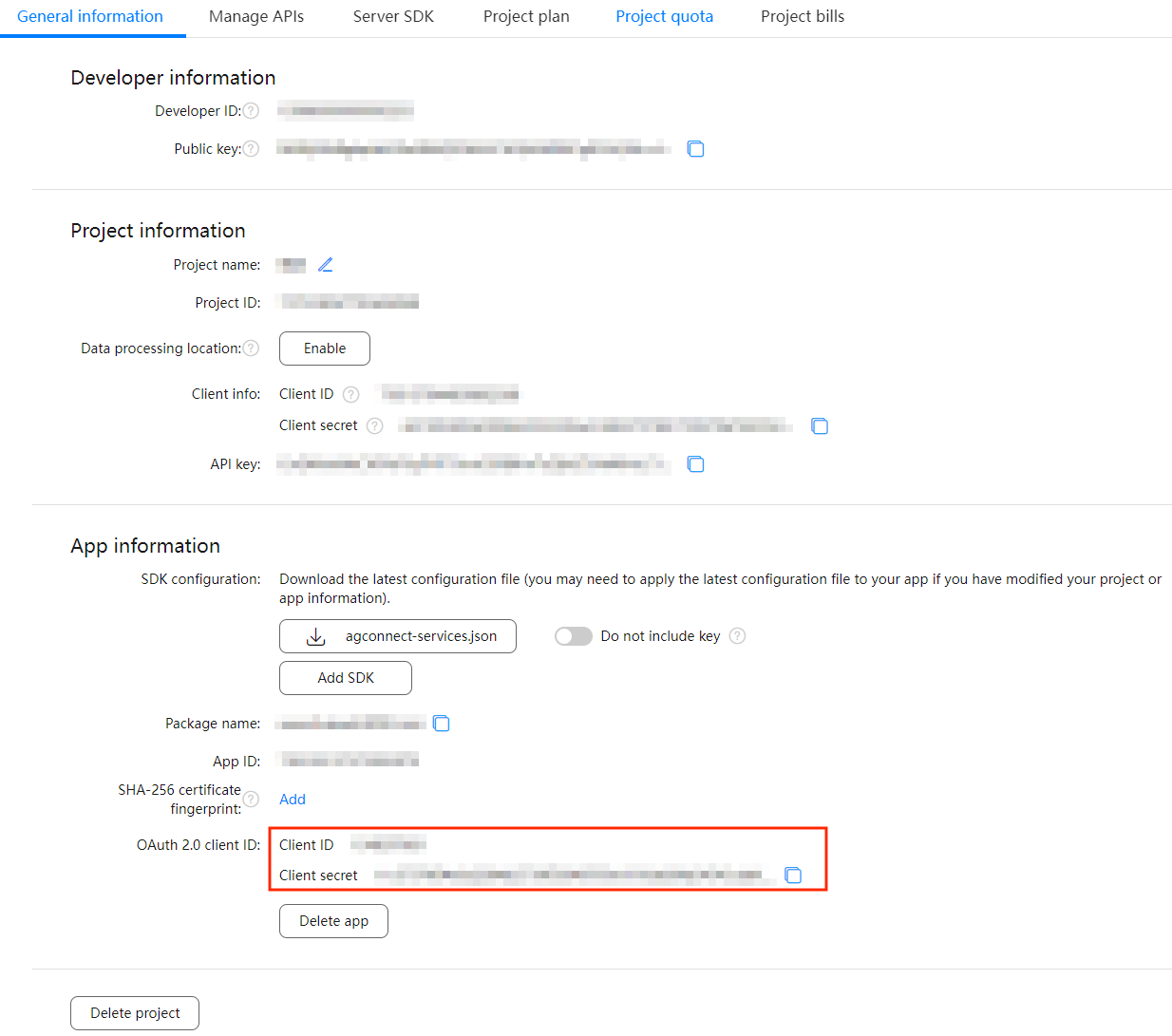
In Huawei App Gallery Connect, navigate to
Project settings>App information>OAuth 2.0 client ID. Locate theClient IDandClient secretcopy their values. You will use these to configure the Huawei Push Service integration in Engagement.
-
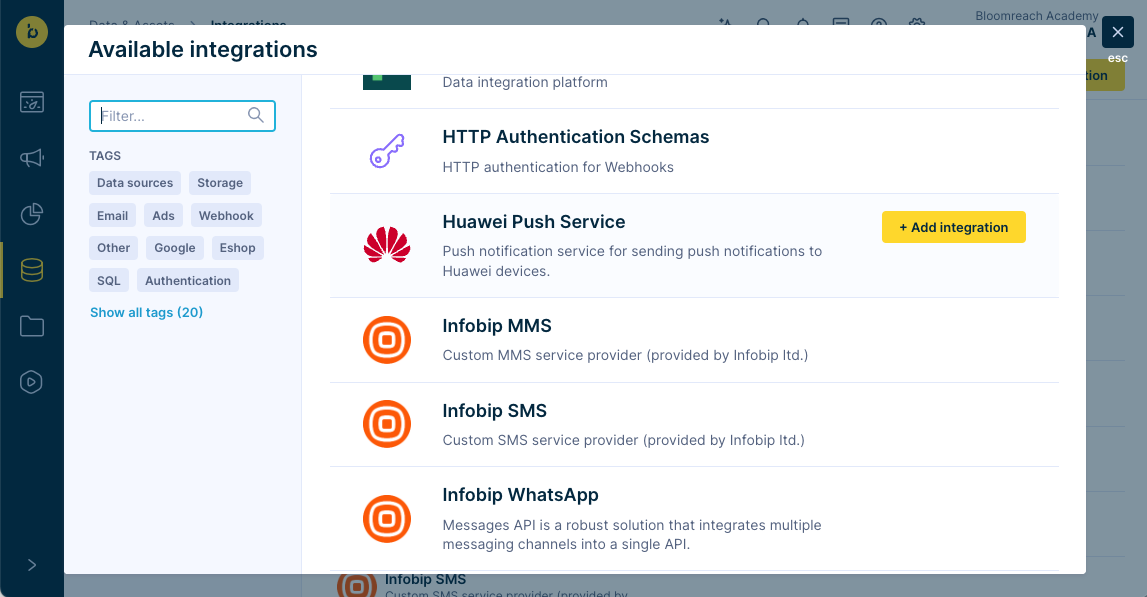
Open the Engagement web application and navigate to
Data & Assets>Integrations. Click+ Add new integration. -
Locate
Huawei Push Serviceand click+ Add integration.
-
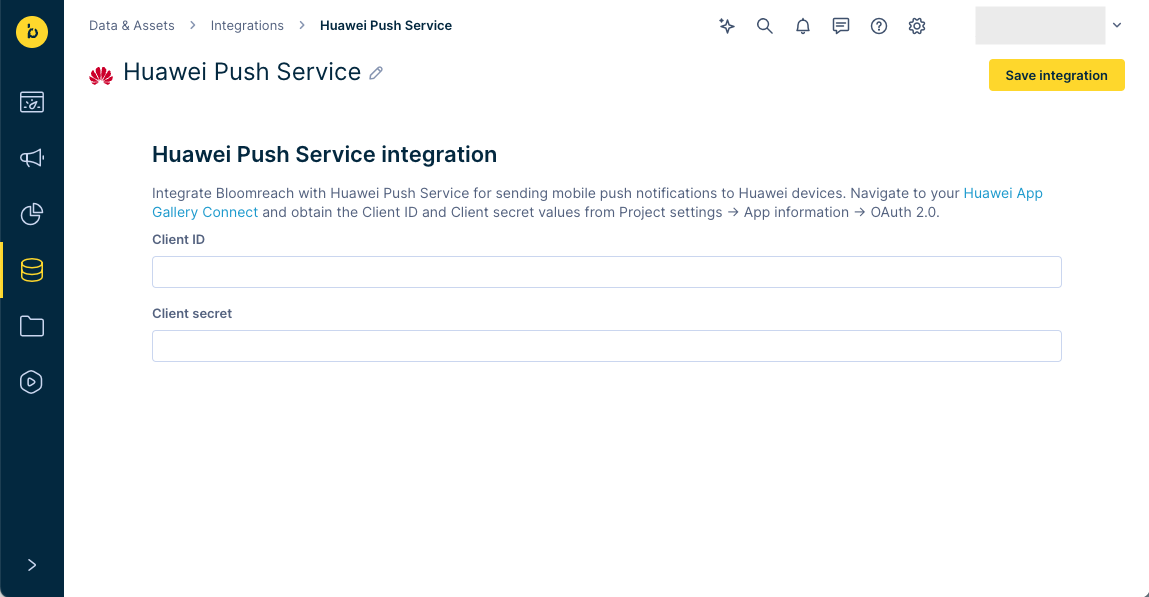
Enter the
Client IDandClient secretvalues you copied in step 1. ClickSave integrationto finish.
-
Navigate to
Settings>Project settings>Channels>Push notifications>Android Notificationsand setHuawei integrationtoHuawei Push Service.
Updated 8 days ago
